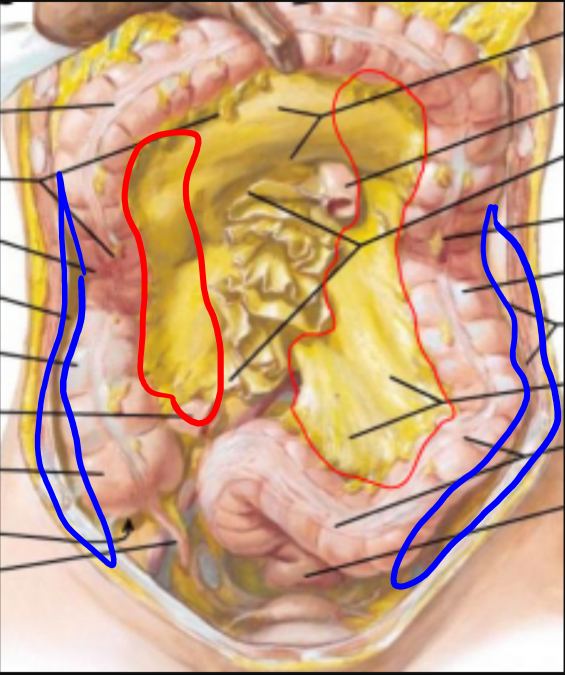
B left upper quadrant window.
Paracolic gutter space bleeding.
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space between the parietal and visceral peritoneum.
Bile pus or blood released from viscera anywhere along its length may run along the gutter and collect in sites quite remote from the organ of origin.
Visualize the left subdiaphragmatic space the most important area in the left upper quadrant splenorenal space and left paracolic gutter.
The inframesocolic space also contains paracolic gutters which are peritoneal recesses that are inferolateral extensions of their corresponding inframesocolic spaces on the posterior abdominal wall lateral to the ascending and descending colon respectively.
The paracolic spaces gutters are located lateral to the peritoneal reflections of the left and right sides of the colon fig 8a.
It normally contains only a thin film of peritoneal fluid which consists of water electrolytes leukocytes and antibodies.
Visualize the right subdiaphragmatic space hepatorenal recess morison pouch the most sensitive recess for upper abdominal free fluid and the right paracolic gutter.
Fluid from an infected appendix can track up the right paracolic gutter to the hepatorenal recess.
The right and left paracolic gutter are connected to subphrenic spaces proximally and to the pelvic area at the distal end.
What are the paracolic gutters rectouterine pouch retroperitoneal space ulnar gutter subphrenic space abdominal wall hepatic flexure peritoneal space ascendi.
The right paracolic gutter is larger than the left and communicates freely with the right subphrenic space.
It contains the duodenum pancreas and retroperitoneal segments of the ascending and descending colon it also contains the roots of the small bowel mesentery and transverse mesocolon.
This drainage occurs in much the same way that the gutters on a house draw the rain off the roof.
Paracolic gutters function to drain fluid that leaks from the colon such as infectious matter pus or bile and to prevent infection or damage to the outer margin of the colon.
Infected peritoneal fluids get a passageway through these gutters to other compartments of the abdominal cavity.